- Education
- About Forex
- How to Trade Forex in Canada
How to Trade Forex in Canada
Forex trading, also known as foreign exchange trading, is the buying and selling of currencies on the foreign exchange market. It offers individuals the opportunity to potentially profit from fluctuations in currency exchange rates. In Canada, forex trading is regulated by the Investment Industry Regulatory Organization of Canada (IIROC), which ensures the protection of investors. If you're interested in trading forex in Canada, this article will guide you through the process.

What is Forex CFD?
Before delving into the specifics of forex trading in Canada, it's important to understand the concept of Forex CFD (Contract for Difference). Forex CFDs allow traders to speculate on the price movements of currency pairs without actually owning the underlying currencies. Instead, traders enter into an agreement with a broker to exchange the difference in the value of a currency pair between the opening and closing of a trade.
How to Trade Forex in Canada
1. Educate Yourself
The first step in trading forex in Canada is to educate yourself about the forex market and its various intricacies. Familiarize yourself with concepts such as currency pairs, pip values, leverage, and margin requirements. There are numerous online resources, courses, and tutorials that can help you gain a solid understanding of forex trading.
Let's explore each concept with examples:
Currency Pairs:
In forex trading, currencies are always traded in pairs. Each currency pair represents the exchange rate between two currencies. For instance, the popular currency pair EUR/USD represents the value of the Euro relative to the US Dollar.
The first currency in the pair is called the base currency, and the second currency is the quote currency. Understanding currency pairs helps traders analyze the relative strength or weakness of different currencies and make informed trading decisions.
Pip Values:
A pip, short for "percentage in point," is the smallest unit by which a currency pair's value can change. It represents the fourth decimal place in most currency pairs. For example, if the EUR/USD pair moves from 1.2500 to 1.2501, it has increased by 1 pip. The monetary value of a pip depends on the lot size and the currency pair being traded. Let's say you're trading a standard lot (100,000 units) of the USD/JPY pair, and the exchange rate moves by 1 pip. Since the quote currency in this pair is the Japanese Yen, the pip value would be 1,000 JPY.
Leverage:
Leverage allows traders to control a larger position in the market with a smaller amount of capital. It is expressed as a ratio and indicates the amount of borrowed funds provided by the broker. For example, a leverage ratio of 1:100 means that for every dollar of your own capital, you can control $100 in the market. While Forex leverage amplifies potential profits, it also magnifies losses. It's crucial to use leverage wisely and consider the associated risks.
Suppose you have $1,000 in your trading account and want to trade with a leverage ratio of 1:100. With this leverage, you can control a position of $100,000. However, keep in mind that while the potential gains are higher, the potential losses are also multiplied.
Margin Requirements:
Margin is the collateral required by the broker to cover potential losses on a trade. It is a percentage of the total value of the position. Margin requirements vary depending on the broker and the currency pair being traded. For example, if a broker requires a margin of 1%, and you want to trade a position worth $100,000, you would need to have $1,000 in your account as margin.
Using the same example as before, if you have $1,000 in your account and want to control a position of $100,000, your margin requirement might be 1% of $100,000, which is $1,000. In this case, you would be using the entire amount of your available margin, so it's important to monitor your trades closely to avoid a margin call.
Understanding these concepts is crucial for managing risk, calculating potential profits and losses, and making informed trading decisions in the forex market. It's important to educate yourself thoroughly and consider practicing with a demo account before trading with real money.
2. Choose a Reliable Broker
To trade forex in Canada, you'll need to select a reputable forex broker. Look for brokers that offer competitive spreads, a user-friendly trading platform, efficient customer support, and secure deposit and withdrawal methods. It's also essential to ensure that the broker provides access to the currency pairs you're interested in trading.
3. Open a Trading Account
Once you've chosen a broker, you'll need to open a trading account. This typically involves completing an online application form, providing identification documents, and agreeing to the broker's terms and conditions. Some brokers may also require a minimum deposit to fund your account.
4. Download a Trading Platform
Most brokers offer trading platforms such as MetaTrader 4 (MT4) or MetaTrader 5 (MT5) for forex trading. These platforms provide real-time market data, charting tools, and various order types to execute trades. After opening your trading account, download and install the preferred trading platform on your computer or mobile device.
5. Develop a Trading Strategy
Successful forex trading requires a well-defined trading strategy. Determine your risk tolerance, preferred trading style (such as scalping, day trading, or swing trading), and the indicators or tools you'll use for market analysis. Backtest your strategy using historical data to assess its performance before applying it in live trading.
6. Start Trading and Manage Risk
With your trading strategy in place, you're ready to start trading forex in Canada. Begin by practicing on a demo account provided by your broker to familiarize yourself with the trading platform and test your strategy in real-time market conditions. Once you feel comfortable, you can switch to a live trading account.
When trading forex, it's crucial to manage your risk effectively. Set appropriate stop-loss and take-profit levels for each trade to limit potential losses and secure profits. Utilize risk management tools offered by the trading platform, such as trailing stops, to protect your trades.
Forex Trading in Canada
Here's an example of a trading strategy for forex trading in Canada:
Trading Strategy: Moving Average Crossover
Objective:
The objective of this strategy is to identify trends in the forex market and enter trades based on the crossover of two moving averages.
Indicators:
- 50-period Simple Moving Average (SMA)
- 200-period Simple Moving Average (SMA)
Entry Rules:
Bullish Signal:
- When the 50-period SMA crosses above the 200-period SMA, it generates a bullish signal indicating a potential uptrend.
- Enter a long trade (buy) when the bullish crossover occurs.
Bearish Signal:
- When the 50-period SMA crosses below the 200-period SMA, it generates a bearish signal indicating a potential downtrend.
- Enter a short trade (sell) when the bearish crossover occurs.
Exit Rules:
Take Profit:
Set a predetermined profit target based on your risk-reward ratio. For example, if you have a risk-reward ratio of 1:2, set your take profit level at twice the distance of your stop loss level from your entry point.
Stop Loss:
Place a stop loss order below the recent swing low in a long trade (buy) and above the recent swing high in a short trade (sell). This helps limit potential losses if the trade moves against you.
Risk Management:
Position Size:
Determine your position size based on your risk tolerance and the percentage of your trading account you're willing to risk on a single trade. For example, if you're willing to risk 2% of your account per trade, calculate your position size accordingly.
Risk-Reward Ratio:
Maintain a favorable risk-reward ratio to ensure that potential profits outweigh potential losses. For example, if your stop loss is set at 50 pips, your take profit should be set at 100 pips.
Example Trade:
Let's say you're trading the USD/CAD currency pair and using the moving average crossover strategy. You notice a bullish crossover, where the 50-period SMA crosses above the 200-period SMA. You enter a long trade at 1.3048. Your stop loss is set at 1.3000, 48 pips below your entry, and your take profit is set at 1.3800, 752 pips above your entry. If the trade reaches your take profit level, you would gain 752 pips. However, if the trade hits your stop loss, you would lose 48 pips.
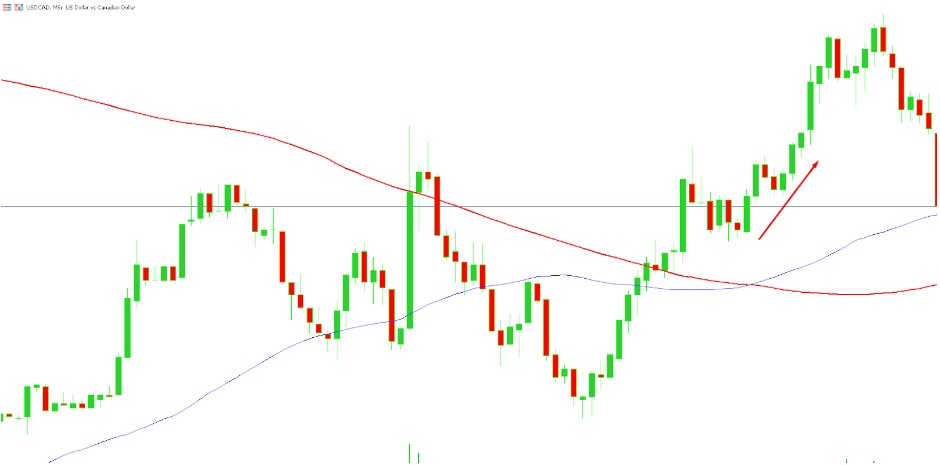
In this case the price went as high as 1.3842 but your take profit was a bit lower and you gained 752 pips instead of 794 pips.
Remember, this is just one example of a trading strategy, and it's important to conduct thorough backtesting and adapt the strategy to fit your trading style, risk tolerance, and preferred currency pairs. Additionally, make sure to monitor your trades and adjust your strategy as market conditions change.
Bottom Line on How to Trade Forex in Canada
Trading forex in Canada can be an exciting and potentially profitable venture. However, it's important to approach it with the right knowledge, skills, and mindset. Educate yourself about the forex market, choose a reliable broker, open a trading account, download a trading platform, develop a trading strategy, and manage risk effectively.
Remember to start with a demo account and gradually transition to live trading. With practice and discipline, you can increase your chances of success in the forex market.

